This article has been just updated: January 17, 2024
The memory requirements of applications and games have increased dramatically over the years. The computer that put man on the moon in 1969, the so-called Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC), had approximately 64 KB of memory and operated at 0.043MHz. Today, you need at least a few GB of memory and a powerful processor with multiple cores just to read the news on the web.
 For more than a decade DDR3 RAM ruled the market. First introduced in 2007, this type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth interface comes in several variants, including ECC memory with an extra data byte lane used for correcting minor errors and detecting major errors for better reliability.
For more than a decade DDR3 RAM ruled the market. First introduced in 2007, this type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth interface comes in several variants, including ECC memory with an extra data byte lane used for correcting minor errors and detecting major errors for better reliability.
But the reign of DDR3 RAM is slowly but surely coming to an end as the demand for DDR4 RAM increases.
“This cutting-edge memory is the foundation for the next-generation of devices. DDR4 enables developers to add more powerful processors to their hardware. For consumers, that means advanced computing capabilities on all platforms, whether it’s a smartphone, tablet or desktop computer,” explains Lenovo.
 Released to the market in 2014, DDR4 RAM introduces a number of benefits over DDR3 RAM, but they come at a price. In this article, we explain the main differences between DDR3 and DDR4 memory to help you decide whether DDR4 is really worth the upgrade.
Released to the market in 2014, DDR4 RAM introduces a number of benefits over DDR3 RAM, but they come at a price. In this article, we explain the main differences between DDR3 and DDR4 memory to help you decide whether DDR4 is really worth the upgrade.
Technical Differences
| Voltage | Bus Clock | Internal Rate | Transfer Rate | Channel Bandwidth | |
| DDR | 2.50 V | 100-200 MHz | 100-200 MHz | 0.20-0.40 GT/s | 1.60-3.20 GBps |
| DDR 2 | 1.80 V | 200-533 MHz | 100-266 MHz | 0.40-1.06 GT/s | 3.20-8.50 GBps |
| DDR 3 | 1.50 V | 400-1066 MHz | 100-266 MHz | 0.80-2.13 GT/s | 6.40-17.0 GBps |
| DDR 4 | 1.20 V | 1066-2133 MHz | 100-266 MHz | 2.13-4.26 GT/s | 12.80-25.60 GBps |
 DDR4 RAM is not backward compatible with older generations of RAM because of major differences in its physical design. For starters, DDR4 has switched to a 288-pin interface, whereas DDR3 RAM uses a 240-pin interface. The extra pins increase the bandwidth capacity of DDR4 RAM. But you might not be able to tell that DDR4 RAM modules have 44 additional pins compared with DDR3 RAM modules because the pin-to-pin distance has been brought from 1.00 mm down to 0.85 mm.
DDR4 RAM is not backward compatible with older generations of RAM because of major differences in its physical design. For starters, DDR4 has switched to a 288-pin interface, whereas DDR3 RAM uses a 240-pin interface. The extra pins increase the bandwidth capacity of DDR4 RAM. But you might not be able to tell that DDR4 RAM modules have 44 additional pins compared with DDR3 RAM modules because the pin-to-pin distance has been brought from 1.00 mm down to 0.85 mm.
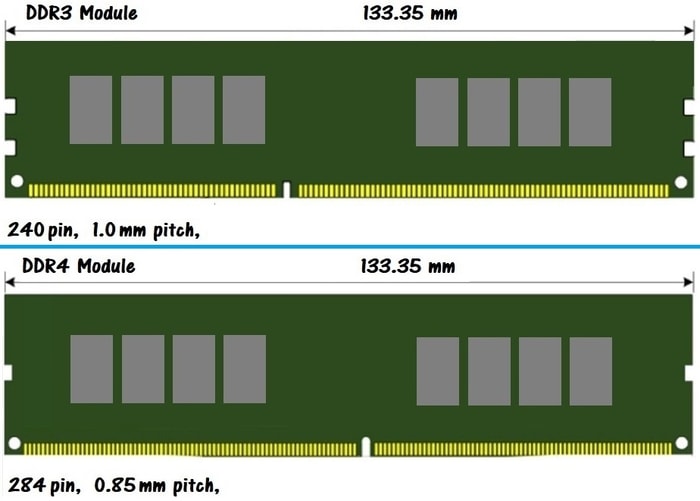 Bare DDR4 RAM modules have a height of 31.25 mm, as compared to DDR3’s 30.35 mm. In practice, the less-than-a-millimeter difference in height means absolutely nothing because virtually all high-performance memory modules released in the last decade are equipped with a heatsink.
Bare DDR4 RAM modules have a height of 31.25 mm, as compared to DDR3’s 30.35 mm. In practice, the less-than-a-millimeter difference in height means absolutely nothing because virtually all high-performance memory modules released in the last decade are equipped with a heatsink.
A single DDR3 memory module can be only 8 GB large, but DDR4 memory modules have no such limitation. This makes DDR4 RAM perfect for video editing and other memory-intensive applications, giving you the option to add an absurdly large amount of RAM even to a fairly standard motherboard with just four memory slots.
But perhaps the most important physical difference between DDR4 and DDR3 RAM is that DDR4 runs at only 1.2 volts, down from 1.5 volts. The relatively minor difference in voltage translates into around 15 saved watts for a typical system, and you can probably imagine just how much electricity can DDR4 RAM save massive server farms with thousands of individual memory modules.
Performance Comparison
As you can see in the chart above, the transfer rate of DDR3 RAM starts at 0.80 GT/s and caps at a little over 2 GT/s. On the other hand, the transfer rate of DDR4 RAM starts at 2.13 GT/s and ends at over 4 GT/s.
Unfortunately, the increased transfer rate comes with an increase in latency. A DDR3 RAM module operating at a latency of CL11 takes about 13.75 nanoseconds to initiate a read, but most DDR4 RAM modules operate at a latency of CL15 or CL16, so they take approximately 2 percent longer to initiate a read.
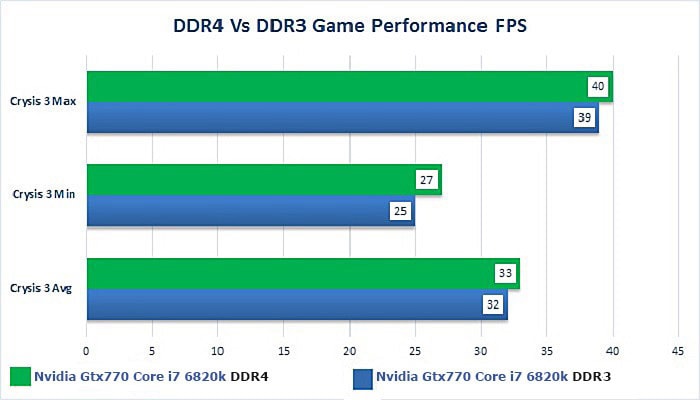 What do these performance numbers mean in practice? A small but measurable performance gain in favor of DDR4 RAM when playing games and working with memory-intensive applications, such as Adobe Premiere CC, Autodesk 3ds Max, AutoCAD, or even Google Chrome.
What do these performance numbers mean in practice? A small but measurable performance gain in favor of DDR4 RAM when playing games and working with memory-intensive applications, such as Adobe Premiere CC, Autodesk 3ds Max, AutoCAD, or even Google Chrome.
More importantly, DDR4 RAM is more stable because it operates at a lower voltage and applies it consistently to each individual memory chip. You probably won’t appreciate the improved stability when editing documents, watching movies, listening to music, or browsing the web. But you’ll definitely appreciate it when rendering video, compiling software, or even playing competitive games.
Compatibility and Pricing
As we’ve already explained, DDR4 memory is not backward compatible with DDR3 memory. That means two things:
• First, you can’t mix and match DDR4 and DDR3 memory modules.
• Second, you can not use DDR4 memory with a motherboard with slots for DDR3 memory.
Because the performance gains of DDR4 memory aren’t massive, it doesn’t make much sense to upgrade to it unless the rest of your system is ready for an upgrade as well. But if you’ve been itching to build a new computer, DDR4 memory is the way to go.
 Even though it’s been around for just a few years, it now costs almost the same as DDR3 memory. For example, the CORSAIR Vengeance LPX 8GB DDR4 memory module costs $59.99, while its DDR3 counterpart is just $10 cheaper. So, if you get two for a total of 16GB of DDR4 memory, you’ll pay only $20 extra, which isn’t bad at all considering the improved performance of DDR4 memory, its lower power consumption, and its future-proof design.
Even though it’s been around for just a few years, it now costs almost the same as DDR3 memory. For example, the CORSAIR Vengeance LPX 8GB DDR4 memory module costs $59.99, while its DDR3 counterpart is just $10 cheaper. So, if you get two for a total of 16GB of DDR4 memory, you’ll pay only $20 extra, which isn’t bad at all considering the improved performance of DDR4 memory, its lower power consumption, and its future-proof design.
Verdict
DDR4 RAM improves virtually all aspects of DDR3 RAM. It has a much higher transfer rate, operates at a lower voltage, is more stable, and brings minor but measurable performance gains when working with memory-intensive applications.
If you’re generally happy with your computer and could only just a few GB of extra RAM, there’s no need to throw away your current motherboard just so you can use DDR4 RAM. But if you’re building a new computer from scratch, DDR4 is the way to go. Just be sure to also get a fast SSD, so you can enjoy your fast memory without constantly running into bottlenecks caused by your slow storage device.
FAQ
What are the fundamental differences between DDR3 and DDR4 RAM?
DDR3 and DDR4 are types of RAM with several key differences. DDR4 has a higher data rate, lower voltage, and improved stability compared to DDR3. DDR4 operates at 1.2V, while DDR3 operates at 1.5V (or 1.35V for DDR3L). DDR4 also starts at 2133 MHz, which is considered the base speed, whereas DDR3 speeds typically start at 1066 MHz.
How does the voltage difference between DDR3 and DDR4 affect energy consumption?
The lower voltage of DDR4—1.2V compared to the 1.5V of standard DDR3 or 1.35V of DDR3L—means DDR4 consumes less power and generates less heat. This can lead to energy savings and potentially extend the lifespan of a computer’s components.
In what way does DDR4’s increased data rate translate to real-world performance gains?
DDR4’s higher data rate means it can process more data per second than DDR3, leading to better performance in memory-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and data analysis. In practice, users may see quicker application response times and faster data transfer speeds.
Can DDR3 be used in a DDR4 motherboard or vice versa?
No, DDR3 and DDR4 are not cross-compatible. Each type of memory has a different key notch position to prevent inserting the wrong type of memory into an incompatible motherboard, ensuring that only the correct memory type can be used.
What are the main benefits of DDR4’s improved stability over DDR3?
DDR4 integrates features like improved refresh algorithms and on-die termination (ODT) which enhance signal integrity and reduce noise, making it more stable and reliable than DDR3 at higher speeds, especially in systems under heavy loads.
How does DDR4’s increased transfer rate affect gaming performance compared to DDR3?
For gaming, DDR4’s higher transfer rates can result in smoother performance, particularly in games that are heavily reliant on quick memory operations. However, the actual performance gain may vary depending on the specific game and the overall system configuration.
Is there a significant cost difference when choosing DDR3 over DDR4, and how should this affect purchasing decisions?
Historically, DDR4 was more expensive than DDR3, but as DDR4 has become the standard, the price difference has decreased. When building or upgrading a system, it’s often better to opt for DDR4 for future-proofing, despite any slight cost increase.
Are there any compatibility issues when upgrading from DDR3 to DDR4?
Because DDR3 and DDR4 use different sockets and chipsets, you cannot simply replace DDR3 with DDR4 in an existing motherboard. An upgrade would typically require a new motherboard (and potentially a new CPU) that supports DDR4 memory.
How do DDR3 and DDR4 compare in terms of latency?
DDR4 tends to have higher latency than DDR3 due to its higher density and speed capabilities. However, the overall better performance and higher data rates of DDR4 often offset the impact of the increased latency.
What is the maximum memory capacity available with DDR3 and DDR4?
DDR4 has a higher theoretical maximum capacity per DIMM compared to DDR3. While most DDR3 modules are limited to 8 or 16 GB, DDR4 modules can come in capacities up to 64 GB, allowing for more RAM in a single system.
In terms of multitasking, how does DDR4 compare with DDR3?
With its higher speed and larger capacity potential, DDR4 can handle more simultaneous processes than DDR3. This allows for a smoother multitasking experience, as systems can keep more data readily accessible without needing to swap to slower storage.
What improvements does DDR4 bring to power management over DDR3?
Apart from lower operating voltage, DDR4 includes additional features for power management, like a deeper sleep mode and more efficient background operations, that promote reduced overall power consumption.
How do server and enterprise environments benefit from DDR4’s performance compared to DDR3?
Servers and enterprise environments, which require high reliability and performance under heavy loads, benefit significantly from DDR4’s higher transfer rates and improved error-correcting technologies, enhancing overall system performance and stability.
What advancements in DDR4 technology contribute to its higher speed?
DDR4 incorporates a range of advancements such as a higher bus frequency, improved data prefetching, and a more efficient architecture, which collectively enable its higher speeds.
Can the performance differences between DDR3 and DDR4 be noticed in everyday computing tasks?
While DDR4 generally offers better performance, the differences might not be noticeable in basic everyday computing tasks. However, in applications that are memory-intensive or for users who demand high performance, DDR4’s benefits can become more apparent.
Are there any environmental consequences of using DDR3 over DDR4?
Considering DDR4’s lower power consumption, it is arguably more environmentally friendly than DDR3. By consuming less electricity, DDR4 can potentially reduce the carbon footprint of data centers and personal computing.
What futureproofing advantages does DDR4 offer over DDR3?
As DDR4 is the current standard and supports higher speeds, capacities, and efficiency, it offers better futureproofing. Investing in DDR4 will ensure compatibility with newer hardware and software for a longer period than DDR3.
Does DDR4 offer any specific advantages in laptops and portable devices?
Yes, DDR4’s lower power consumption translates to longer battery life in laptops and portable devices. The reduced heat generation also helps with maintaining better thermal management in the constrained spaces of portable systems.
What impact does DDR4’s higher bandwidth have on big data and analytics workloads?
The higher bandwidth of DDR4 allows for faster processing of large data sets, which is crucial for big data and analytics applications. It enables quicker insights and response times for data-intensive workloads.
How does the release of DDR5 affect the DDR3 vs DDR4 comparison?
The introduction of DDR5 will likely widen the performance and efficiency gap between DDR3 and DDR4, by offering even higher speeds and capacities. Although DDR5 is now the cutting edge, DDR4 remains a more economical and tested choice for most existing systems. You can find more information on the newest DDR technology standards.